
What is a Right Angle
When we talk about the Pythagorean theorem, we are dealing with right triangles. Let’s take a deep dive into what a right triangle is. Take a look at the different types of triangles below.

| A | B | C |
| Right triangle | Acute triangle | Obtuse triangle |
When we refer to these types of triangles, we are talking about their angles. Recall that an angle is formed by two lines. The units used for angles are called degrees. Let’s take a look at the most important angles.

| A | B | C | |
| Degrees | 90 | 180 | 360 |
As you can see, an angle is anything between 0 and 360 degrees. When we talk about triangles, we classify them by the type of angle they have. That is, the largest angle they have.
| Type | Degrees |
| Acute angle | 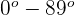 |
| Right angle | 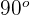 |
| Obtuse angle | 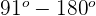 |
So when we talk about right triangles, we’re talking about triangles whose largest angle is exactly 90 degrees.
Pythagorean Theorem
Right triangles are important in maths because they have very special properties. The Pythagorean theorem states that the square of the longest side of the triangle is the sum of the squares of the other two sides.

| c | Longest side |
| a & b | Other two sides |
Okay, sounds complicated right? Well, it’s actually quite simple. Let’s look at an example.

| Definition | Location | |
| Hypotenuse | The longest side in a right triangle | The side that is opposite of the right angle |
In our example above, since the right angle is located opposite to the last side, we know that the last side is our hypotenuse.

 , which means to get c we simply need to take the square root.
, which means to get c we simply need to take the square root. 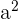 | 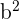 | c |
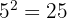 | 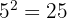 | 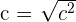 = =  |
While the Pythagorean theorem may seem pretty random, it actually can be understood visually. Let's pretend that each side of a right triangle was actually just one side of a square.

Example 1
A factory that makes LEGOs is interested in producing triangle shaped LEGOs. These triangles will be part of a set that allows anyone to make a car. In order to make the car out of these LEGOs, each piece has to fit perfectly together.
You are in charge of the inspection of these triangle shaped toys. Every triangle must be a right triangle in order to fit correctly. You take a sample of the triangles made, which is displayed below.
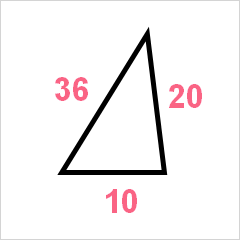
| Largest Side (C) | A | B |
| 36 | 10 | 20 |
To verify whether this triangle has a right triangle, we can simply plug the numbers into the formula to see whether the squares of the smaller sides add up to the square of the bigger side.
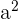 | 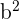 |  | 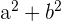 |
| 100 | 400 | 1296 | 100+400 = 500 |
Because 500 doesn’t equal 1296, we can say this triangle is not a right triangle and fails the test.
Example 2
You have a square fence in your backyard. Unfortunately, a new development has decided to build apartments behind your neighborhood. Their development will cut across your backyard. While you will get compensated, they will need you to give them the price of the new fence.
Here are the details of your backyard.

In addition to this, although we only know the length of one side, we know that squares have the same length for all sides. So, we end up with the following.

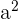 | 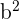 | c |
 |  | 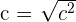 = = 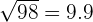 |
Now, we know that the missing side is about 9.9 meters. So the final cost will be 20*9.9 = 198 pounds.
Trigonometric Properties
You may be wondering what you can do to find the sides when you only have information on one side. When we have a right-angle, we can use other properties of right triangles. These properties are called trigonometric properties.

| Condition 1 | Must know the length of one side |
| Condition 2 | Must know one angle |
We already know that the side that is opposite a right triangle is called a right triangle. However, what’s up with the other two sides? Let’s take a look.
| Opposite | The side opposite of the angle (that’s not the right angle) |
| Adjacent | The side next to the angle (that’s not the right angle) |
Note that these can change depending on which angle we have. The only thing that doesn’t change is where the hypotenuse is, because it’s always opposite the right angle.

Sin( ) ) |  |
Cos( ) ) |  |
Tan( ) ) |  |
An easy way to remember this is to remember the acronym: SOHCAHTOA.
| SOH | Sine, Opposite, Hypotenuse |
| CAH | Cosine, Adjacent, Hypotenuse |
| TOA | Tangent, Opposite, Adjacent |













I’m just curious if the area between the polygon and the circumscribed circle has a name.
https://www.superprof.co.uk/resources/academic/maths/geometry/plane/orthocenter-centroid-circumcenter-and-incenter-of-a-triangle.html