Chapters

What is a Sequence?
In order to understand what a sequence is, you should first understand two very important concepts. These two concepts are defined below.
| Numeric Pattern | A numeric pattern is a trend that you can see in a group of numbers | Even numbers have a pattern: 2, 4, 6, 8 |
| Successive | Successive is another way of saying one after another | 1, 2, 3, 4 - in this example, 2 comes immediately after 1; 3 after 2, etc. |
Now, let’s define a sequence. A sequence is defined as a list of numbers that follow a pattern. This pattern can be any of the following described in the table below.
| Random pattern | A pattern that is not strictly defined by the below | 2, 6, 9, 13, 16 |
| Function | A function | f(x) = 2x + 5 |
| Arithmetic | The same number is added | 2, 5, 8, 11 |
| Geometric | Multiplied by the same number | 3, 6, 12, 24 |
While there is no single way to check whether something is a sequence or not, you can usually tell by subtracting or dividing each successive number by the previous number.

Increasing Monotonic Sequence
There are a couple of different ways we can define a sequence. The most common way is to see whether a sequence is a monotone sequence or not. A monotone sequence has only one pattern. It is defined as the following:

In an increasing monotonic sequence, each number after the first number, represented by  , is bigger than the one before it. Let’s take a look at an example.
, is bigger than the one before it. Let’s take a look at an example.
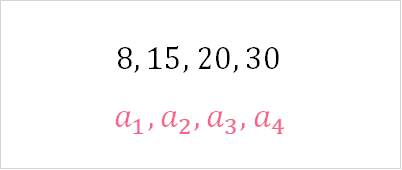
In this example, you can see that there are 4 numbers, represented by the subscript in 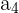 . Each successive number is greater than the one before it. This is defined as a strictly increasing monotonic sequence. Check out the table below for the definition.
. Each successive number is greater than the one before it. This is defined as a strictly increasing monotonic sequence. Check out the table below for the definition.
| Strictly Increasing |  | Each successive number is only greater than the previous one | 2, 4, 6, 8 |
| Weakly Increasing | 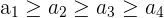 | Each successive number can be greater or equal to the previous one | 2, 2, 4, 6 |
Decreasing Monotonic Sequence
A decreasing monotonic sequence is a similar concept to an increasing monotonic sequence. In a decreasing monotonic sequence, each number after the first number, represented by  , is less than the one before it. Let’s take a look at an example.
, is less than the one before it. Let’s take a look at an example.
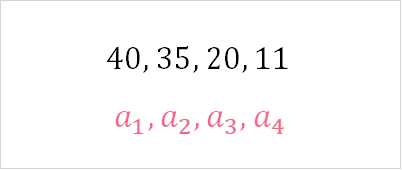
In this example, you can see that there are 4 numbers, represented by the subscript in 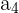 . Each successive number is less than the one before it. This is defined as a strictly decreasing monotonic sequence. Check out the table below for the definition.
. Each successive number is less than the one before it. This is defined as a strictly decreasing monotonic sequence. Check out the table below for the definition.
| Strictly Decreasing | 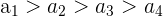 | Each successive number is only less than the previous one | 8, 6, 4, 2 |
| Weakly Decreasing | 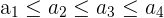 | Each successive number can be less than or equal to the previous one | 6, 4, 2, 2 |
Finite Sequence
A finite sequence is defined as a sequence that has an end. When we write the notation for any sequence, we usually talk about an ‘nth’ term.
This notation is the same as saying:
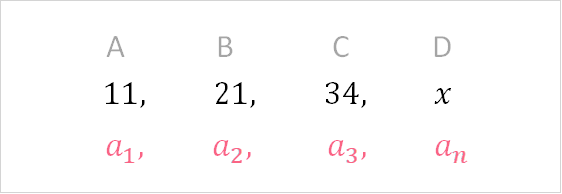
| A | B | C | D |
| 1st | 2nd | 3rd | nth |
A finite sequence is a sequence that has an nth term. No matter how large that nth term is - whether it’s the 100th term or the 1,000,000th term, the sequence is still considered finite if it has a value that we know.
Infinite Sequence
An infinite sequence is similar to a finite sequence in that we can have as many terms as we would like. The only difference is that an infinite sequence has an unknown, or uncountable, end.
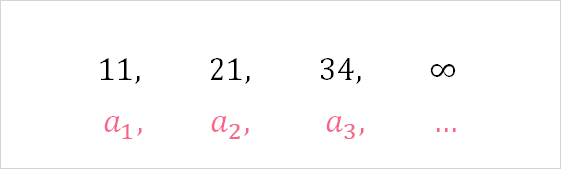
As you can see, instead of ending with 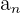 , an infinite sequence ends with infinity.
, an infinite sequence ends with infinity.
Arithmetic Sequence
An arithmetic sequence is defined as a sequence where each successive number is added by a constant.

In this case, we have the following:
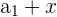 |  | 1 + 3 = 4 |
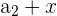 |  | 4 + 3 = 7 |
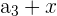 | 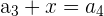 | 7 + 3 = 11 |
Here, we add 3 to every nth number. Notice that the output of the first row becomes the input for the second row, and so on. It is easy to tell whether a sequence is arithmetic or not because you can simply subtract every  from
from 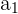 to see if it’s the same number.
to see if it’s the same number.
Geometric Sequence
A geometric sequence is similar to an arithmetic sequence. It is defined as a sequence where each successive number is multiplied by a constant.

In this case, we have the following:
 | 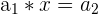 | 1 * 3 = 3 |
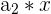 | 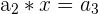 | 3 * 3 = 9 |
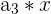 | 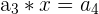 | 9 * 3 = 27 |
Here, we multiply 3 to every nth number. Notice that the output of the first row becomes the input for the second row, and so on. It is easy to tell whether a sequence is geometric or not because you can simply divide every  from
from 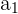 to see if it’s the same number.
to see if it’s the same number.
Difference between Series and Sequence
Sequences and series go hand-in-hand. While a sequence is a list of objects that have a pattern, a series is the sum of a sequence. Let’s take a look at a simple example:














