Chapters
In this article, we will discuss the orthocenter, centroid, circumcenter, and incenter of a triangle. But before discussing these important characteristics of a triangle, first, let us see what is a triangle.

Introduction
A triangle is defined as:
A three-sided polygon that has three edges and three vertices
One of the most important characteristics of a triangle is that the sum of interior angles of a triangle is always equal to 180 degrees. If XYZ is a triangle, then we can denote its as 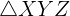 . Here, X, Y, and Z are three vertices of the triangle XYZ.
. Here, X, Y, and Z are three vertices of the triangle XYZ.
As we have already mentioned above that a triangle is a polygon having three sides. Two sides of the triangle are connected end to end to create the vertex of a triangle. An angle is also created between two sides. A triangle is classified into different types based on its angles. One of the most important concepts in trigonometry is the Pythagoras theorem. This theorem is based on the properties of the angles of triangle.
In the next section, we have summarized some of the important properties of a triangle.
Properties of Triangle
Every geometrical figure in mathematics has some unique properties which differentiate that figure from others. A triangle also has its unique properties which set it apart from other figures. Some of the properties of the triangle are discussed below:
- A triangle consists of three sides and three angles. The sum of three interior angles of a triangle is always equal to 180 degrees.
- The sum of exterior angles of the triangle is always equal to 360 degrees.
- The aggregate of consecutive interior and exterior angles is always equal to 180 degrees which means they are supplementary
- If the lengths of two sides of a triangle are added together, then the resultant sum is always greater than the length of the third side.
- The difference between the length of the two sides of the triangle is always lesser than the length of the third side.
- The side opposite to the smallest interior angle of a triangle is always the shortest side of the triangle.
- The side opposite to the largest interior angle of the triangle is always the longest side of the triangle
In the next section, we will discuss the orthocenter, centroid, circumcenter, and incenter of a triangle.
Orthocenter
The orthocenter of a triangle is defined as:
The point of intersection of the three heights of a triangle
Or
The point where all the three altitudes of the triangle meet or intersect each other.
An altitude or height is each of the perpendicular lines drawn from one vertex to the opposite side (or its extension).
See the following triangle. Point H is the orthocenter of this triangle because it is the point where all the three altitudes of the triangle are intersecting each other.
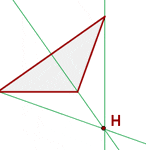
The orthocenter is different for various triangles such as isosceles, scalene, equilateral, and acute, etc. For an equilateral triangle, the centroid will be the orthocenter. In the case of other types of triangles, the position of the point where all the three altitudes intersect will vary.
- The orthocenter of an acute triangle lies inside the triangle
- The orthocenter of an obtuse triangle lies outside the triangle
- The orthocenter of a right-angled triangle lies on the vertex of the right angle
Centroid
The centroid is defined as:
The point of intersection of the three medians.
A median refers to the straight line that joins the midpoint of a side with the opposite vertex.
A centroid has the following properties:
- A centroid refers to the center of an object and it is the center of gravity
- It always lies inside the triangle
- It is the point of intersection or concurrency of three medians of the triangle
A centroid of the triangle is shown in the figure below:

The centroid divides each median into two segments, the segment joining the centroid to the vertex is twice the length of the line segment joining the midpoint to the opposite side. In the case of the above triangle, we can denote it as:
BG = 2GA
Hence, we can conclude that a centroid segregates the median of the triangle in the ratio of 2 : 1. We can find the centroid of a triangle by calculating the average of x- coordinate points and y - coordinate points of all three vertices of a triangle.
For instance, consider the following example:
Find the centroid of a triangle whose vertices are (3, 4), (5, 7), and (4, 7).
To find the centroid, we need to take the average of x-coordinates and y - coordinates separately.
Average of x - coordinates = 
Average of Y - coordinates = 
Hence, the centroid of the triangle is (4, 6)
Circumcenter
The circumcenter of the triangle is defined as:
The point of intersection of the three perpendicular bisectors.
A perpendicular bisector of a triangle is each line drawn perpendicularly from its midpoint. The circumcenter is the center of a triangle's circumcircle (circumscribed circle). A circumcenter of the triangle is shown in the figure below:
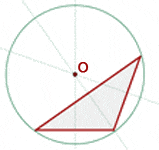
- The circumcenter of a triangle is the center of a circumcircle
- All the three vertices of the triangle are equidistant from the circumcenter of a triangle
- The circumcenter lies inside the acute-angled triangle
- The circumcenter lies outside the obtuse-angled triangle
- Circumcenter in a right-angled triangle lies at the midpoint of the hypotenuse side
Incenter
The incenter of a triangle is defined as:
The point of intersection of the three angle bisectors
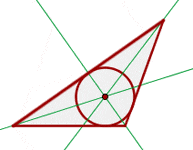
The angle bisectors of a triangle are each one of the lines that divide an angle into two equal angles. The incenter is the center of the circle inscribed in the triangle.
Thus, we can say that the incenter of a triangle is the intersection point of all the three angle bisectors of a triangle. The incenter is always equidistant from the three sides of the triangle.
The incenter of a triangle is shown in the figure below:
Line of Euler
The orthocenter, the centroid, and the circumcenter of a non-equilateral triangle are aligned. It means that they lie on the same straight line, called a line of Euler.
You can see in the below figure that the orthocenter, centroid and circumcenter all are lying on the same straight line and are represented by O, G, and H. This straight line is the line of Euler.














I’m just curious if the area between the polygon and the circumscribed circle has a name.
https://www.superprof.co.uk/resources/academic/maths/geometry/plane/orthocenter-centroid-circumcenter-and-incenter-of-a-triangle.html