Chapters

What is a Limit?
When we want to find the limit of something, we are generally trying to find the limit of a function. You can think of a limit as the boundary of a function. Take a look at the following example.

| x | y |
| 1 | 0.0625 |
| 2 | 0.003906 |
| 3 | 0.000244 |
| ... | ... |
| 8 | 2.33E-10 |

When we plug in bigger and bigger values into x for this function, we can see it gets closer and closer to zero.
Limit Notation
When we are asked to find the limit of a function, there is a certain notation we encounter. Let’s take a look at this notation.

| A | Symbol for the limit |
| B | As the inputs, x, approach a specific value a |
| C | The function we want to find the limit for |
The notation for approaching the value a on the right and left can be found below.
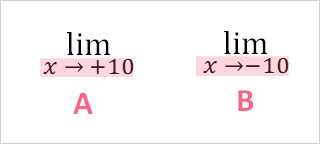
| A | B |
| Approach from right side | Approach from left side |
Approach from the Left
Sometimes, the function at the specified value a doesn’t exist. Take a look at some examples below.
| Function | Results is Unknown |
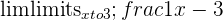 | 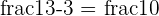 |
 | 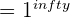 |
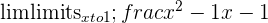 |  |
When this happens, we can instead get as close to the specific value a as possible. Take a look.

| x | y |
| 0.8 | 1.8000 |
| 0.9 | 1.9000 |
| 0.99 | 1.9900 |
| 0.999 | 1.9990 |
| 0.9999 | 1.9999 |
As we approach 1, we see that our value gets closer and closer to 2. We can say that our limit is 2.
Approach from the Right
In the previous section, we wanted to approach 1. So, we plugged in values that were closer and closer to 1. In that example, we approached 1 from the left side. Take a look at why:

We can also approach our a value from the right side. Take a look at the result.
| x | y |
| 1.1 | 2.1000 |
| 1.01 | 2.0100 |
| 1.001 | 2.0010 |
| 1.0001 | 2.0001 |
As you can see, we get the same result: as we approach 1 form the right side, we get closer and closer to two.
Indeterminate Forms
Indeterminate forms have unknown values. This means we do know their true value, whether they are undefined or simply unknown. We can typically divide common indeterminate forms into three groups.
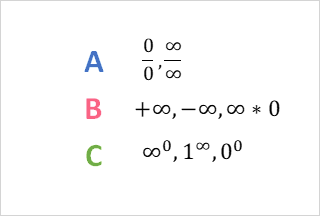
| A | B | C |
| Fraction | Standard | Power |
Problem 1
In this problem, we will review what you have learned about indeterminate forms. Given the following table, label each limit that will result an indeterminate form as a approaches 0.
| 1 | 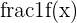 |
| 2 | 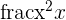 |
| 3 |  |
Problem 2
Take a look at the following limit problem.

Taking what you’ve learned about approaching limits, approach the value a from the right. Next, approach the value a from the left.
Problem 3
Taking what you know about finding the limit, lets try to find the limit of a function as it approaches infinity.

Keep in mind that for this problem you might have to approach the limit form the right or left, depending on what result you get.
Problem 4
In this problem, we will put together some more knowledge on indeterminate forms. Take the following function.
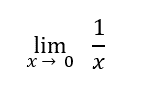
Find the limit of the function and then graph the function as it approaches its limit.
Solution Problem 1
In this problem, you were asked to review what you learned about indeterminate forms. Given table, you had to label each limit that will result an indeterminate form as a approaches 0.

| 1 | 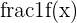 |  | Indeterminate form |
| 2 | 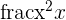 |  | Indeterminate form |
| 3 |  |  | Regular |
Solution Problem 2
In this problem, you were asked to look at the limit problem and approach the value a from the right and from the left.
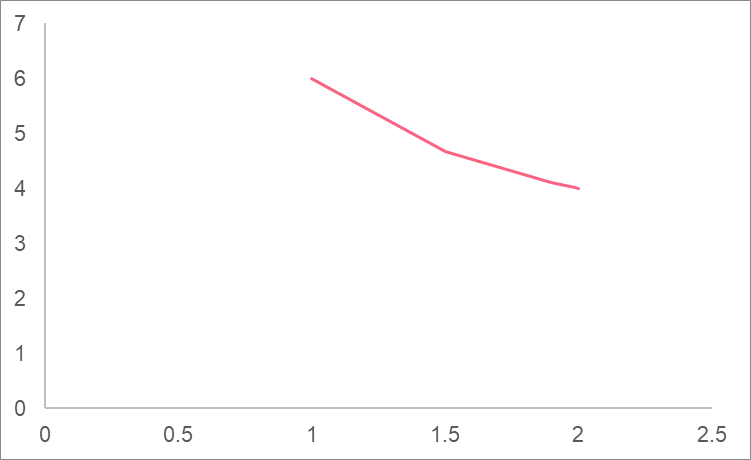
First, we plug in values that approach 2 from the left.
| x | y |
| 1 | 6 |
| 1.5 | 4.666667 |
| 1.9 | 4.105263 |
| 1.99 | 4.01005 |
| 1.999 | 4.001001 |
Here, we can see the y value gets closer and closer to 4.
Let’s approach the value 2 from the right now and see if the same pattern occurs.
| x | y |
| 2.001 | 3.999 |
| 2.01 | 3.990 |
| 2 | 4.000 |
| 2.1 | 3.905 |
| 2.5 | 3.600 |
Here, we’re also getting closer to 4.
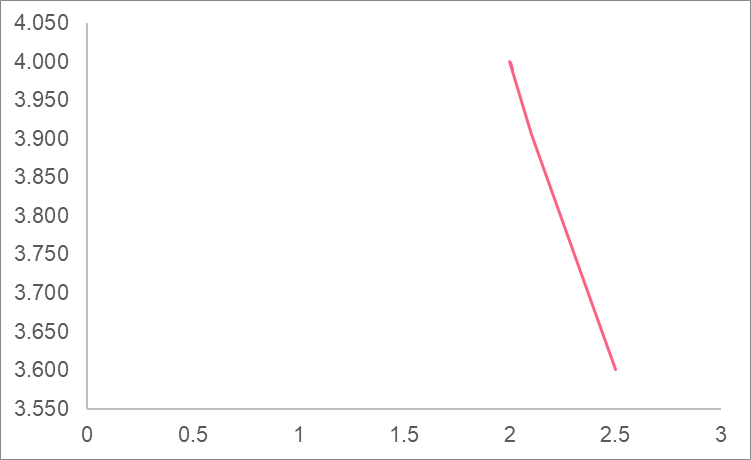
We can see the approach from the right side.
Solution Problem 3
In this problem, you were asked to take what you learned about finding the limit and use it to try to find the limit of a function as it approaches infinity. In this problem, we didn’t specify whether you had to approach the limit form the right or left.
Let’s first plug infinity into the problem.

Here, we encounter a problem: infinity is endless and therefore unknown/undefined. However, we can approximate infinity by plugging in higher and higher values into this 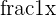 term.
term.
| x | y |
| 10 | 0.1 |
| 100 | 0.01 |
| 1000 | 0.001 |
| 90000 | 1.11E-05 |
As you can see, when we approach higher and higher values of x, we get closer and closer to zero.
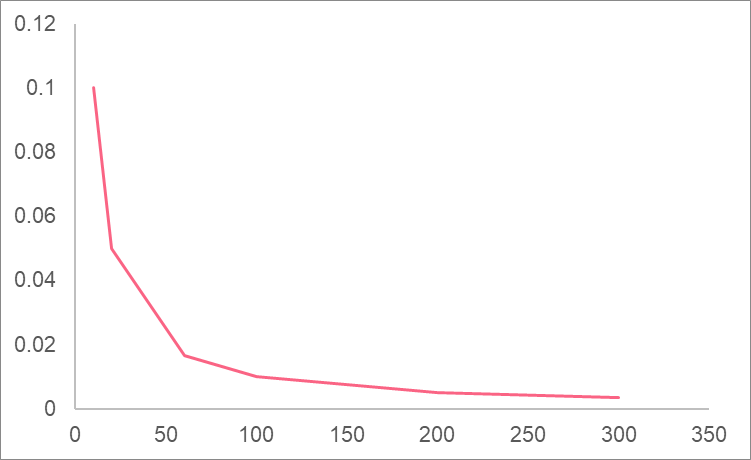
Because this term is approximately zero, we can say that the limit is approximately 2.
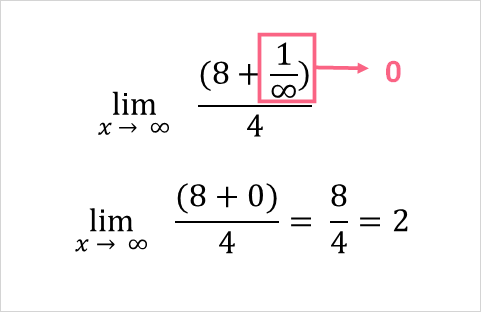
Solution Problem 4
In this problem, we were asked to find the limit of the function and then graph the function as it approaches its limit. We can already see that plugging in this a value will result in an indeterminate form.
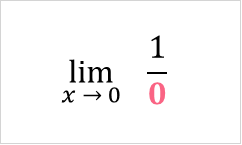
However, we can try plugging in values that approach zero into the x place.
| x | y |
| 1 | 1 |
| 0.5 | 2 |
| 0.01 | 100 |
| 0.001 | 1000 |
| 0.0001 | 10000 |
We can see that as we plug in smaller and smaller values, the y value approaches bigger and bigger numbers. We can also see this visually:

Without using l’Hopital’s rule for finding the limit of indeterminate forms, we can say that as x approaches zero, the limit approaches infinity.













Correct equals infinity equals 16 but not true. It’s it’s six it’s infinity.
And this, my friends, is why humans will be conquered by AI… so many logic holes it’s… well, infinite. lol
Is 0^infinity ( zero to the power infinity) indeterminate form? How?
Didn’t Cantor proved that there are a group of infinities (the Aleph zero & Aleph one sets, for example)? And these are grouped around the concept of infinite to the power infinity, if I remember correctly .
Exercise 3
I think it is discontinuous at 0
exercise 2 : the function is not defined for x= 0.
exercise 1 q 5 The function has a jump discontinuity at x = 1, should be x=0.