Chapters
In this article, we will discuss how to calculate the area between two functions. We will specifically concentrate on how to calculate the area between a curve and a straight line, and the area between two curves.

Area Between Two Functions
The area between two functions is equal to the area of the function located above minus the area of the function that lies below. Mathematically, we can denote this area like this:

Area Between a Curve and a Straight Line
Now, let us understand how to compute the area between a curve and a straight line through the following examples
Example 1
Find the area of the space bounded by the parabola 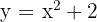 and the straight line that passes through the points A(−1, 0) and B(1, 4).
and the straight line that passes through the points A(−1, 0) and B(1, 4).
Solution
Step 1 - Find the equation of a straight line
In this step, we will calculate the equation of a straight line passing through two points A and B. To do so, first, we should calculate the slope of the line that passes through the points A(-1, 0) and B(1, 4). To calculate the slope, we will use the following formula:
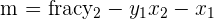
Substitute the values of the points A and B in the above formula:
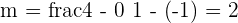
Now, substitute this slope in the point intercept equation below:
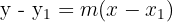
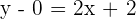

Hence, the equation of the straight line is y = 2x + 2.
Step 2 - Sketch the graph
In this step, we will sketch the graph of the function 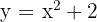 and line
and line  like this:
like this:
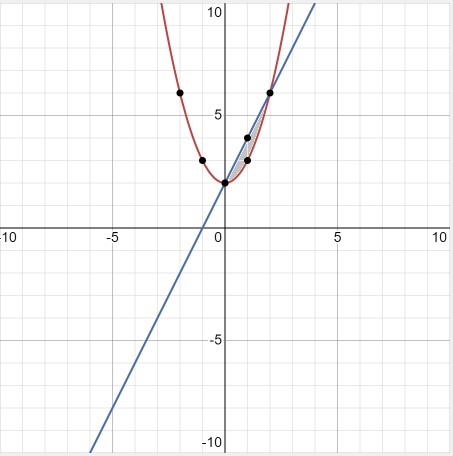
Step 3 - Calculate the boundaries
The points at which the line intersect the parabolas will be the boundaries or limits of the function. As we can see from the above graph, that the line intersects the parabola at  and
and  . Hence, these are limits of the function.
. Hence, these are limits of the function.
Step 4 - Calculate the definite integral
To calculate the definite integral, first, use the information from the previous steps to write the functions in the following form:

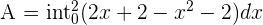
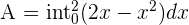
Rewrite the function 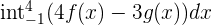 by using the sum/difference rule of definite integrals like this:
by using the sum/difference rule of definite integrals like this:
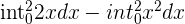
To compute the definite integral, we will first find the antiderivative of the function. The antiderivative of the function is 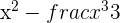
Now, use the fundamental theorem of calculus:
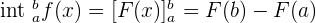
Substitute 2 and 0 in the antiderivative of the function like this:

Example 2
Calculate the area of the figure bounded by the function 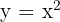 and the lines y = x, at x = 0 and x = 2.
and the lines y = x, at x = 0 and x = 2.
Solution
Step 1 - Sketch the graph
In this example, we are already given the equation of the line y = x. Hence, we don't need to calculate it. We will simply start by sketching the graph of the functions 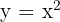 , and
, and  .
.
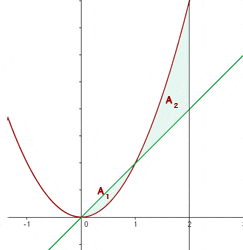
You can see in the above graph that from x = 0 to x = 1, the straight line is above the parabola, and from x = 1 to x = 2, the straight line is below the parabola. Hence, we will compute the areas using these limits above and below the parabola separately.
Step 2 - Calculate the boundaries
The boundaries or limits of the graph are already given in this example which are 0 and 1.
Step 3 - Calculate the definite integral
To calculate the definite integral, first, use the information from the previous steps to write the functions in the following form:

Area where straight line is above the parabola:

Find the antiderivative of the function. The antiderivative of the function is 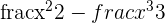
Use the fundamental theorem of calculus:
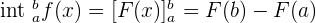
Substitute 1 and 0 in the antiderivative of the function like this:
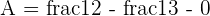
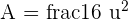
Area where straight line is below the parabola:
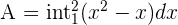
Find the antiderivative of the function. The antiderivative of the function is 
Use the fundamental theorem of calculus:
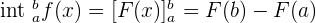
Substitute 2 and 1 in the antiderivative of the function like this:
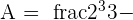 frac{2^2}{2} - frac{1^3}{3} -
frac{2^2}{2} - frac{1^3}{3} - 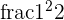

In the next section, we will see how to calculate the area between two curves given their equations.
Area Between Two Curves
The following examples will let you understand how to calculate the area between two curves.
Example 1
Find the area bounded by the graphs of the functions 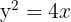 and
and 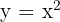
Solution
Step 1 - Sketch the graph

Step 2 - Find the boundaries
To determine where the graphs of two curves intersect each other, we will equate the equations of two curves:
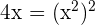

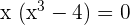
 or
or 
Hence, the boundaries are 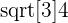 and 0.
and 0.
Step 3 - Calculate the definite integral
To calculate the definite integral, first, use the information from the previous steps to write the functions in the following form:

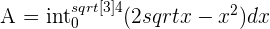
Find the antiderivative of the function. The antiderivative of the function is 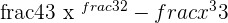
Use the fundamental theorem of calculus:
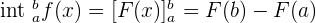
Substitute 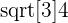 and 0 in the antiderivative of the function will give us the following value of area:
and 0 in the antiderivative of the function will give us the following value of area:

Example 2
Find the area between two curves 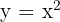 and
and  .
.
Solution
Follow these steps to calculate the area.
Step 1 - Sketch the graph
The graph of the two curves is given below:
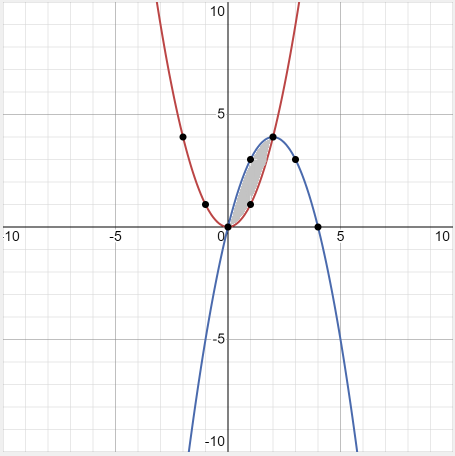
Step 2 - Find the boundaries
Calculate the boundaries of the function by equation both the equations like this:



 or
or 
Hence, the boundaries of the function are 0 and 2.
Step 3 - Calculate the definite integral

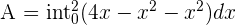

Find the antiderivative of the function. The antiderivative of the function is 
Use the fundamental theorem of calculus:
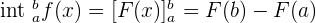
Substitute 2 and 0 in the antiderivative of the function:















